GPU Computing
Today’s central processing units (CPUs) have 4, 8, or even 16 cores, while graphics processing units (GPUs) can have hundreds or thousands of small cores. These highly task-parallel, specialized computing cores are used for graphics processing, having an architecture that is well-suited for parallel computing applications. Using GPUs to perform computation traditionally handled by CPUs (known as general-purpose computing on graphics processing units, or GPGPU) can accelerate compute-intensive applications by spreading computing workloads over multiple cores.

GPU Computing at the Edge
GPUs can boost the performance of a wide range of workloads, including image processing and analysis, compute acceleration, and artificial intelligence (AI). As requirements for responsiveness and accuracy become more demanding for edge systems, the combination of CPUs and GPUs is becoming more mainstream in order to deliver optimal efficiency in performance per watt and dollar.
Image processing and analysis
Air traffic control, electronic chart display and information system (ECDIS), video walls, digital signage, gaming, and healthcare
Compute acceleration
High-performance application processing such as radar/ sonar systems and ultrasound imaging
AI engines
System training and inferencing in smart manufacturing, aerospace and defense
Edge Computing
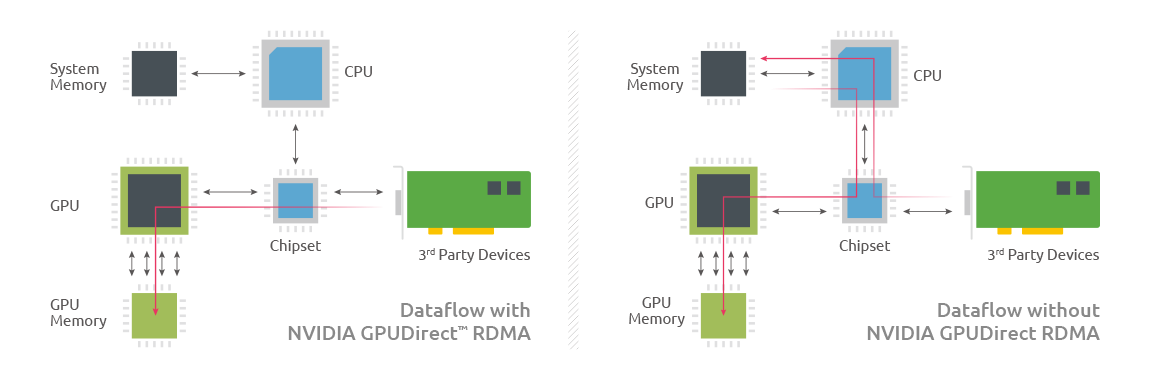
Adding a GPU to an edge system can be complex because satisfying key edge system requirements, such as low system latency, long product availability, and power efficiency, is not an easy task. A common theme in edge application examples is the need to quickly move external data from sensors and other sources to the GPU for processing. ADLINK achieves this by implementing remote direct memory access (RDMA), a feature of NVIDIA GPUDirect® technology in NVIDIA® Quadro® GPUs, that can boost data throughput by approximately 80 percent (3.6 to 6.5 GB/s) and reduce system latency by 60 percent.* RDMA gives external data sources direct access to the GPU’s external memory.
Edge AI
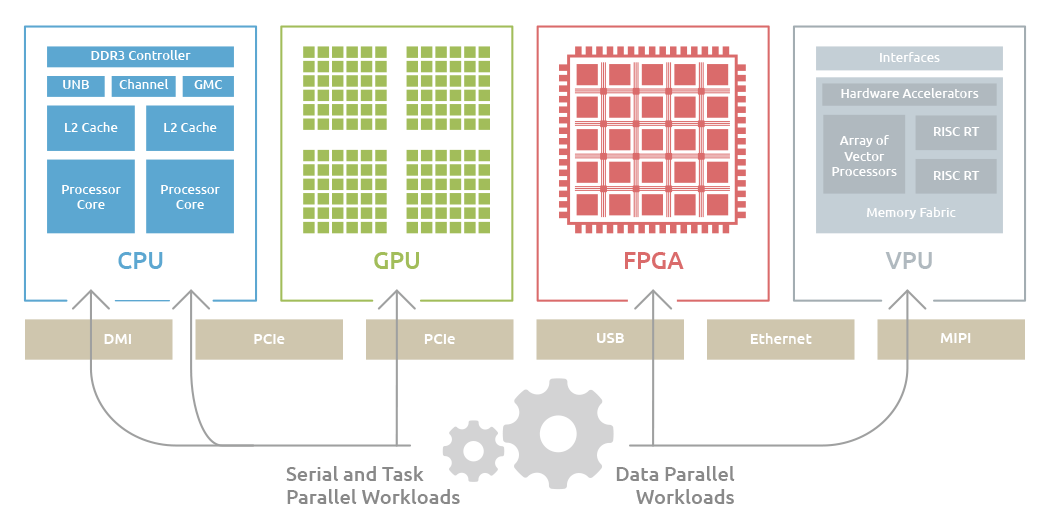
Companies seeking to maximize the innovation and productivity gains from deep learning and AI should consider using a computing platform optimized for the types of algorithms used in these applications. Deep learning and AI algorithms operate with a wide range of inputs including video, text, voice, images, and sensor data where the data is processed sequentially, or in parallel. To handle these diverse requirements, an optimized computing platform will typically employ two or more different types of computing cores to accelerate edge computing and AI workloads. This is where ADLINK’s heterogeneous computing platforms come in.
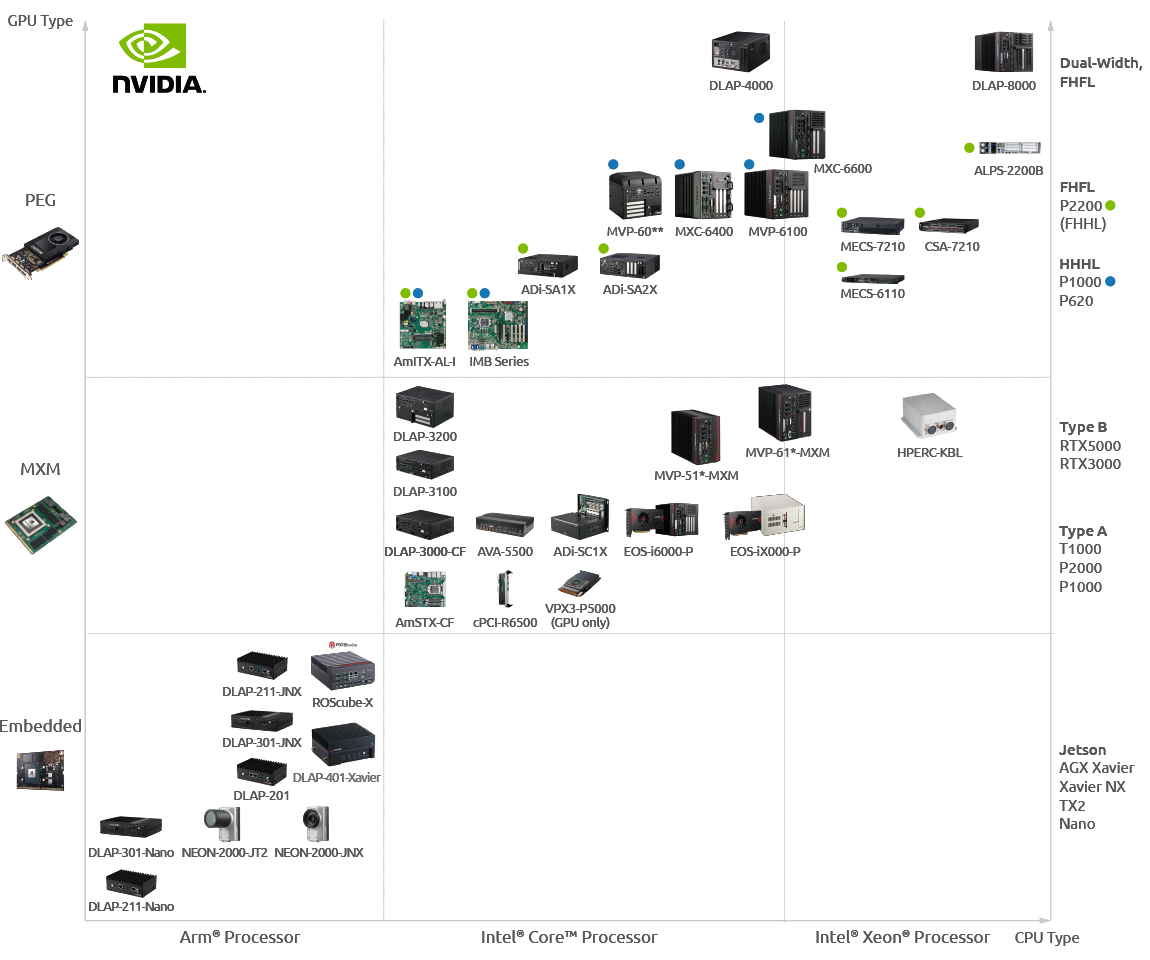
ADLINK’s GPU Solutions
To enable edge systems to tap into the power that can be provided by GPU computing, ADLINK offers a comprehensive portfolio of optimized heterogeneous computing solutions including embedded MXM GPU modules and PCI Express graphics cards, edge AI platforms, GPU computing platforms and other embedded form factors, to satisfy a wide range of embedded requirements based on performance, long life cycle, power consumption, and form factor. With these platforms, system developers, OEMs, and systems integrators can construct and optimize system architecture for edge computing and AI applications…Learn More