| ADLINK Applications: COTS Conduction Cooled CompactPCI for Military Applications | |||||||
 |
Overview: | ||||||
|
Conduction cooled CompactPCI systems offer rugged and reliable COTS solutions for fanless computing systems that are able to perform in the harsh, rugged and confined environments encountered in military applications in land, sea and airborne installations. Conduction cooled CompactPCI blades provide wider operating temperatures, higher shock and vibration tolerance, and longer MTBF than equivalent air-cooled products. An approved conduction cooling mechanical standard for both 6U and 3U CompactPCI boards allows for interoperability between vendors, increasing the choices available to system integrators and allowing them to leverage COTS technology at reduced cost over MIL-Spec systems. |
|||||||
 |
Military Requirements - COTS Solutions: | ||||||
|
CompactPCI is well accepted for military and aerospace applications and is commonly deployed in land, sea and airborne systems. In order to provide more cost-effective solutions to systems integrators, vendors are increasingly using the approach of modifying standard commercial products (COTS - commercial off-the-shelf) to meet the more stringent environmental requirements of defense programs. Using the same "base" design for both commercial and rugged products provides the following advantages:
|
|||||||
 |
Conduction Cooling for CompactPCI: | ||||||
|
Conduction Cooling is the transfer of heat away from a circuit board and its components through a thermally conducting material. Heat is conducted by this material to the system enclosure and dissipated to the external surroundings. Conventional cooling relies on airflow to carry heat away from the device, or in the absence of airflow, is only capable of cooling low power devices. Conduction cooling can provide the necessary heat dissipation when airflow is impractical, such as in sealed enclosures and confined spaces, or when little or no air is available, as in high altitude and underwater applications. The absence of moving parts such as cooling fans in conduction cooled solutions increases reliability and makes them suited for use in mission-critical applications and harsh environments. The thermally conducting material used in these solutions, usually a machined metal cooling plate, provides increased resistance to shock and vibration.
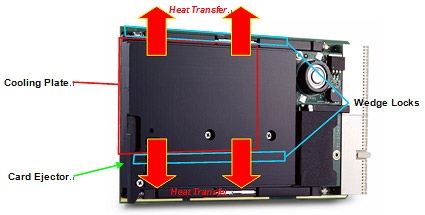
Conduction cooling has been used for rugged computing solutions in military, aviation and aerospace applications for several decades, and is now commonly found in the COTS marketplace, particularly in CompactPCI form factor. The mechanical specification for conduction cooled 3U and 6U CompactPCI systems is defined by the ANSI/VITA 30.1 standard, which evolved from the IEEE-1101.2 mechanical specification for conduction cooled 6U VME cards. VITA 30.1 allows for mechanical compatibility of conduction cooled CompactPCI blades and chassis from different manufacturers. A key rule of the VITA 30.1 standard is that all blades must be capable of insertion into standard, air-cooled CompactPCI chassis. This allows system integrators to begin prototyping conduction cooled systems using commercial chassis and air-cooled peripheral cards, significantly reducing development time. To accommodate I/O expansion on conduction cooled CompactPCI blades using industry standard PCI Mezzanine Cards (PMCs), the VITA 20 specification defines the design rules for Conduction Cooled PMCs (CCPMC) and conduction cooled PMC carrier boards. CCPMCs have a reduced component space that is occupied by thermal and mechanical interfaces to the conduction cooled carrier. To modify a standard CompactPCI blade for conduction cooling, a machined aluminum cooling plate matching the component layout is secured to the board to conduct heat away from components to the card edges, as shown in Figure 2 below. The cooling plate also improves the structural rigidity of the standard commercial blade, minimizing flexing of the board and allowing it to meet shock and vibration requirements for rugged applications.
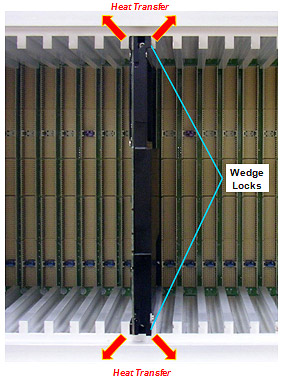
Cooling Plate Functions Thermal - The cooling plate acts as a heatsink for the board components. The underside of the plate is machined to match the component heights and locations on the blade. Heat is carried away to the card edges where a wedge lock mechanism secures the blade inside the chassis and provides a thermal interface to transfer the heat to the chassis and surrounding environment. In conduction cooled applications, the operating temperature of the CompactPCI blade is determined by the temperature at the interface between the wedge locks and the walls of the card slot of the chassis. The mass and heat dissipation properties of the cooling plate effectively lower the operating temperature of the hottest components and average out the temperatures on the blade by transferring heat from hotter to cooler areas. Additionally, by reducing the temperature differences between regions on the board, physical strain resulting from differing thermal expansion coefficients of components and board materials is minimized. This results in improved reliability by increasing MTBF (mean time between failures). Mechanical - The cooling plate covers most of the component side of the blade and provides mechanical support to the entire board. Flexing is reduced and mechanical stiffening provided to increase resistance to shock and vibration. The wedge locks secure the blade to the chassis and minimize motion of the card inside the enclosure.
Conduction cooled systems provide the benefits of allowing sealed enclosures for protection from harmful environments and the ability to operate in confined spaces with little or no airflow. ATR (Air Transport Rack) form factor enclosures have been a de-facto standard for aircraft electronic equipment for over half a decade. ATR enclosures are available in a wide range of case sizes and many COTS conduction cooled ATR chassis for 3U and 6U CompactPCI systems are on the market today. |
|||||||
 |
Military Applications: | ||||||
|
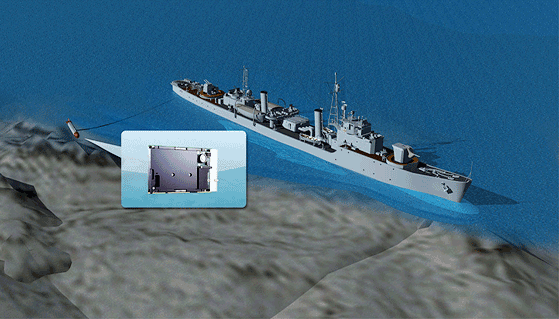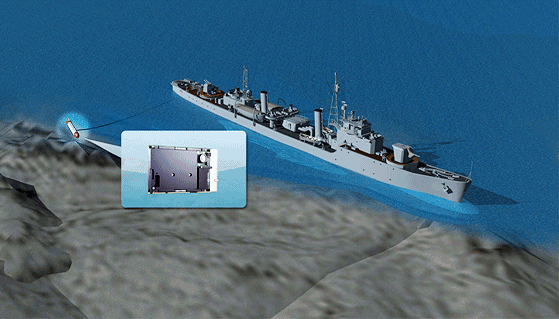
An example of a military application utilizing the advantages of conduction cooling is a remote sonar system towed underwater by a naval vessel. Used for detecting vessels and other objects under water, the sonar system consists of transmitter and receiver transducer arrays and a main transceiver. The sonar system is controlled by an ADLINK CT-31 3U CompactPCI conduction cooled computing blade with a dual-core Intel® Atom™ processor. The CT-31 is accompanied by COTS peripheral cards for data collection and signal processing. The system is housed in a custom sealed enclosure inside the main transceiver. The ADLINK CT-31 provides the required processing power in the limited space available in the towed unit and leverages COTS technology to provide a high performance system at far lower costs than MIL-Spec systems. The CT-31's fanless conduction cooling capability, rugged design and low power consumption allow it to meet the customer's requirements for low noise, high reliability, and the ability to operate in a confined underwater environment.
Radar systems play a crucial role in air defense by providing vital data for timely location of enemy positions. A lightweight mobile weapons vehicle requires a radar system with high computing performance and data transfer rates in order to carry out automatic target recognition and provide computer-based decision aids to the operator. The system is installed in the limited space available in the vehicle with minimal airflow and must be able to withstand the harsh environments of the battlefield. The radar system is controlled by an ADLINK CT-61 6U CompactPCI conduction cooled computing blade which features an Intel® Core™ i7 processor and enables the radar system to perform its mission with high speed, extended range and accuracy. The system is housed in a sealed ATR enclosure and meets the application requirements of a compact size, ruggedness, reliability and wide operating temperature range.
ADLINK Solutions - CT Series ADLINK has developed the "CT Series" of conduction cooled CompactPCI blades in both 3U and 6U sizes. These blades share electronic designs with standard convection cooled models and take advantage of their combined manufacturing volumes. CT Series blades feature an extended operating temperature range and significantly higher shock and vibration tolerance than their conventionally cooled counterparts.
|
|||||||
 |
Conclusion: | ||||||
|
Conduction cooled CompactPCI systems are well suited to military applications and are commonly deployed in land, sea and airborne systems. Conduction cooling meets the unique needs of military environments by providing wider operating temperatures, higher shock and vibration tolerance, and better reliability than equivalent air-cooled products, as well as allowing the use of sealed enclosures and operation in confined spaces with little or no airflow. An approved conduction cooling mechanical standard for CompactPCI provides for interoperability between vendors and allows system integrators to utilize COTS solutions for cost savings over MIL-Spec systems. |
|||||||
 |
|||||||


 operating range.
operating range.
